Economic Goods
Note:
- Normal Good Ordinary Good
- Giffen Good Inferior Good
Depending on Price and Quantity Demanded
- Ordinary Good: Follows the Law of Demand:
- Giffen Good:
- ⇒ Cause: Income Decrease ⇒ Buy cheaper Giffen Good
- Irish Famine. the price of potatoes and meat increased subsequently. Compared to meat, potatoes could be much cheaper as a staple food.
- ⇒ Potatoes were a Giffen Good
Depending on Income and Quantity Demanded
Notation:
- YED:= Income elasticity of demand-
- Income Effect (IE) is important in understanding economic goods
- Normal Good
- i.e. (derivative from Marshallian Demand)
- Necessity Good (Necessities)
- Luxury Good
- …i.e. a normal good for which the proportional consumption increase exceeds the proportional Increase
- Inferior Good:
- i.e.
- Quasilinear Good: doesn’t change on income change
- i.e.
For the set of all goods we can thus show the following Venn diagram:

Game Theory Goods
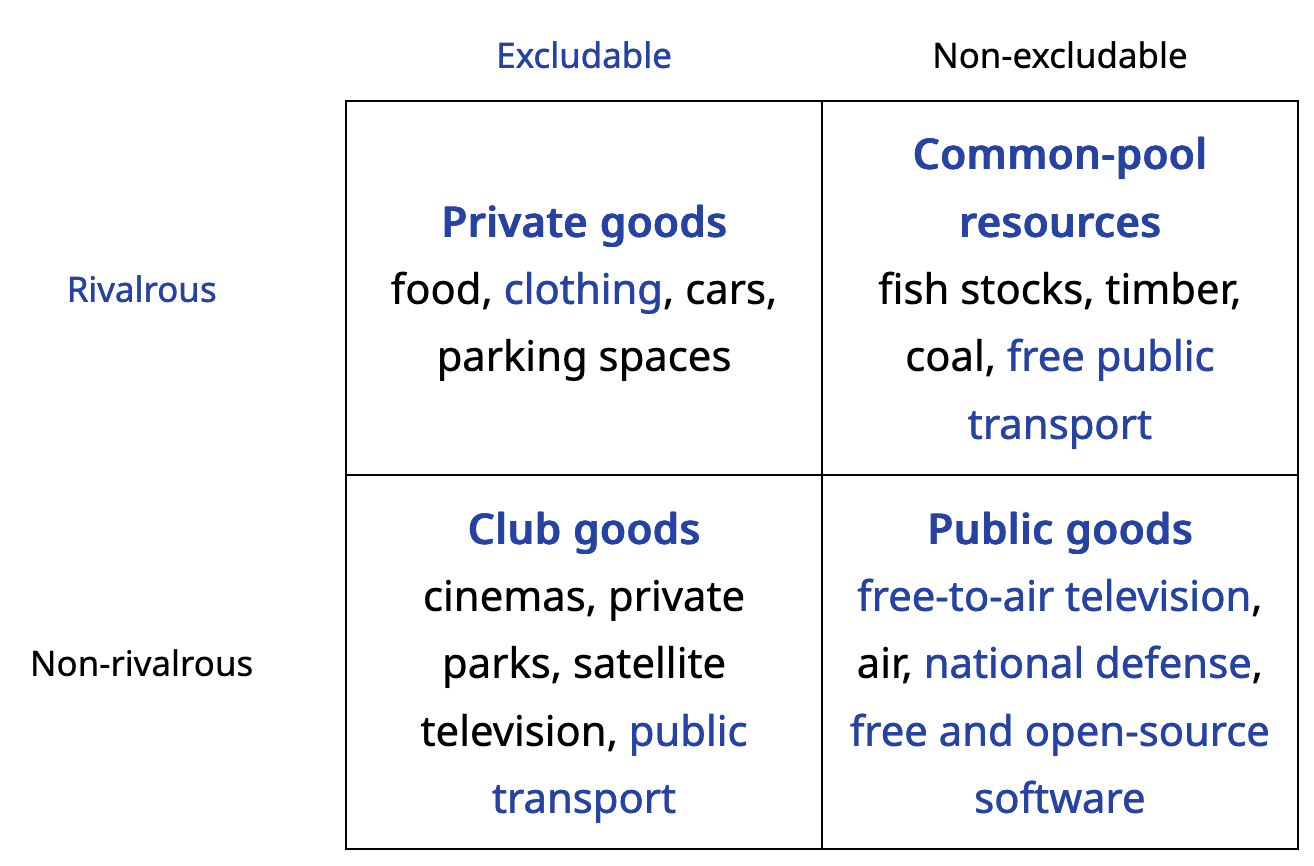
- Common-pool resources are also called Common Goods.
- Public Goods
- The production of a public good is a Prisoner’s Dillemma situation.
- Basic examples: national defense, street lighting, a good schooling district, etc.