Motivation. When a company needs money to invest in a new project, Loans are the simplest way. But banks are wary because once a loan is made they have to keep it to maturity and can’t offload it. We want a loan that is tradable. def. Bonds are loans that are tradable, often of low principle amount, that pays coupon payments (instead of interest, like in loans.) thr. Buying a bond is a way of betting on the current/future interest rates, because , and price of a bond perfectly matches the market yield (linked to federal Fed Funds Rate).
- Tradable Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) are inflation protected bonds.
Cash Flow Structure of a Bond
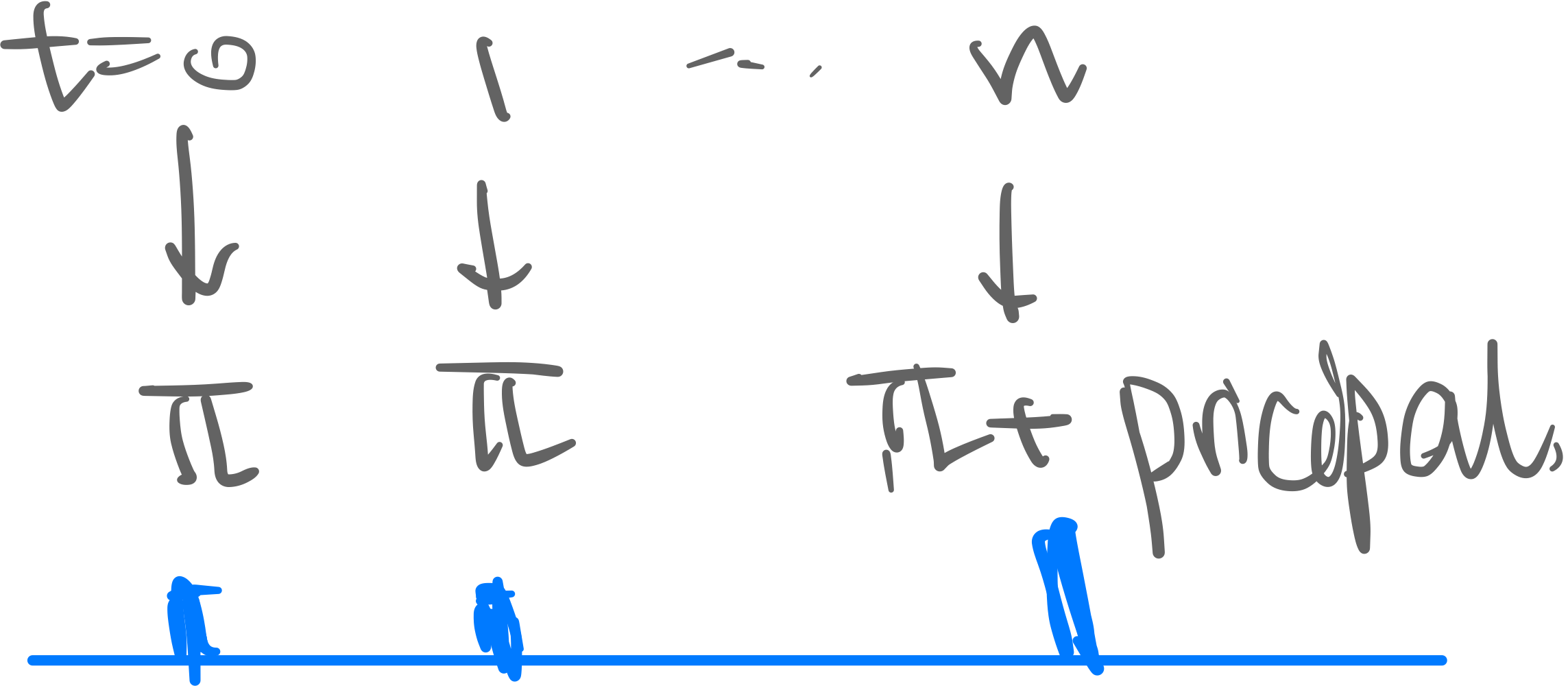
- Lender lends money to the government (usually US Treasury)
- Coupon payments pay regularly:
- Semi-annually for US Treasury
- Annually for other countries
- Principal (=par, base) amount is paid at the maturity;
- Time To Maturity (TTM) is time from now to when the principal pays
- Yield
- Current Yield
- Yield to Maturity: Expectation Hypothesis defines yield to maturity as the expected rate of return if held til maturity.
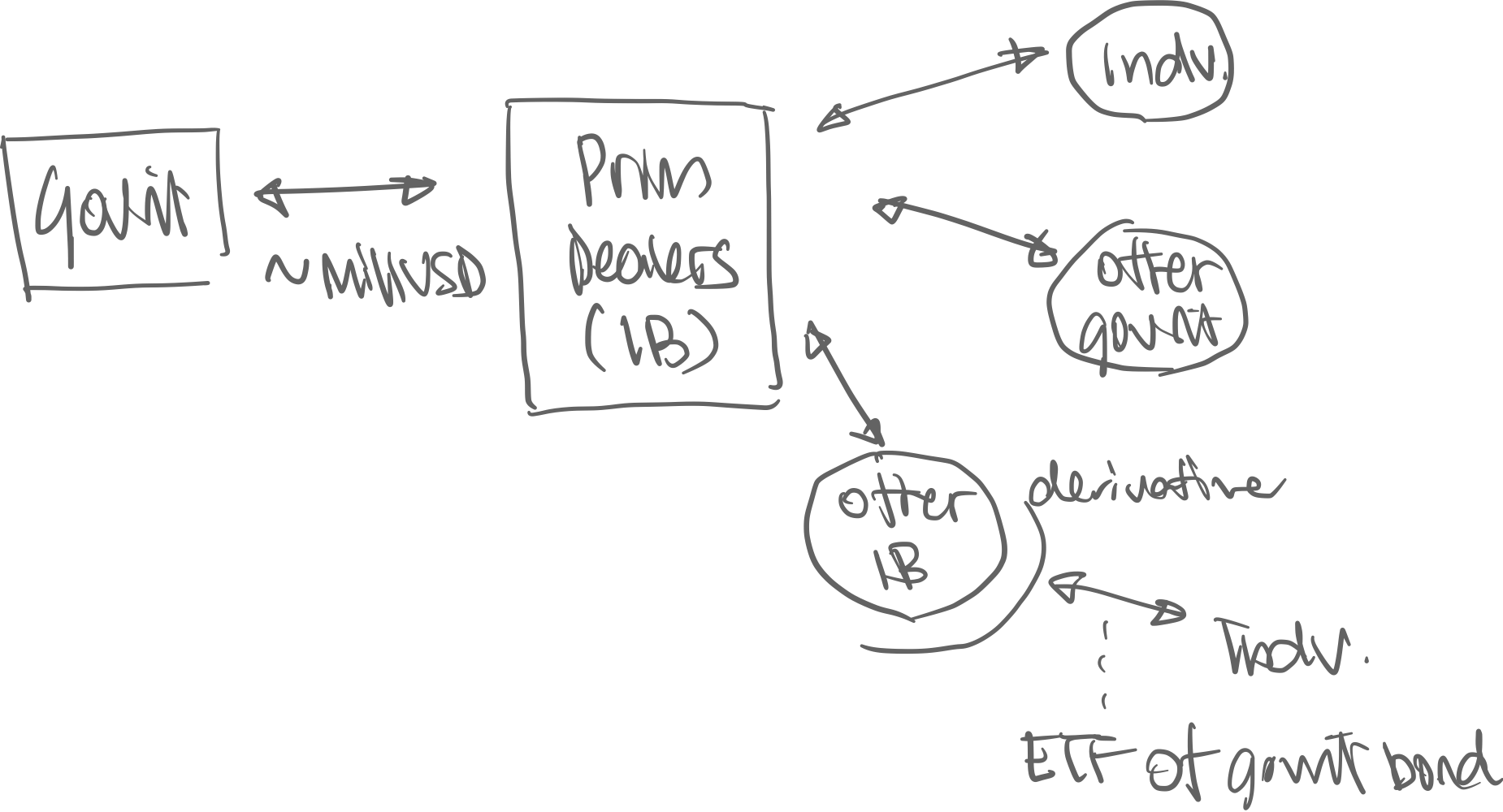
Governments are the borrowers of money in this transaction.
- Government “issues” bonds regularly, which is
- Primary Market: Treasury sells bonds (millions of $ worth) mostly to private Investment Banks
- Secondary Market: Investment banks sell smaller chunks to private investors / bond holders sell to each other
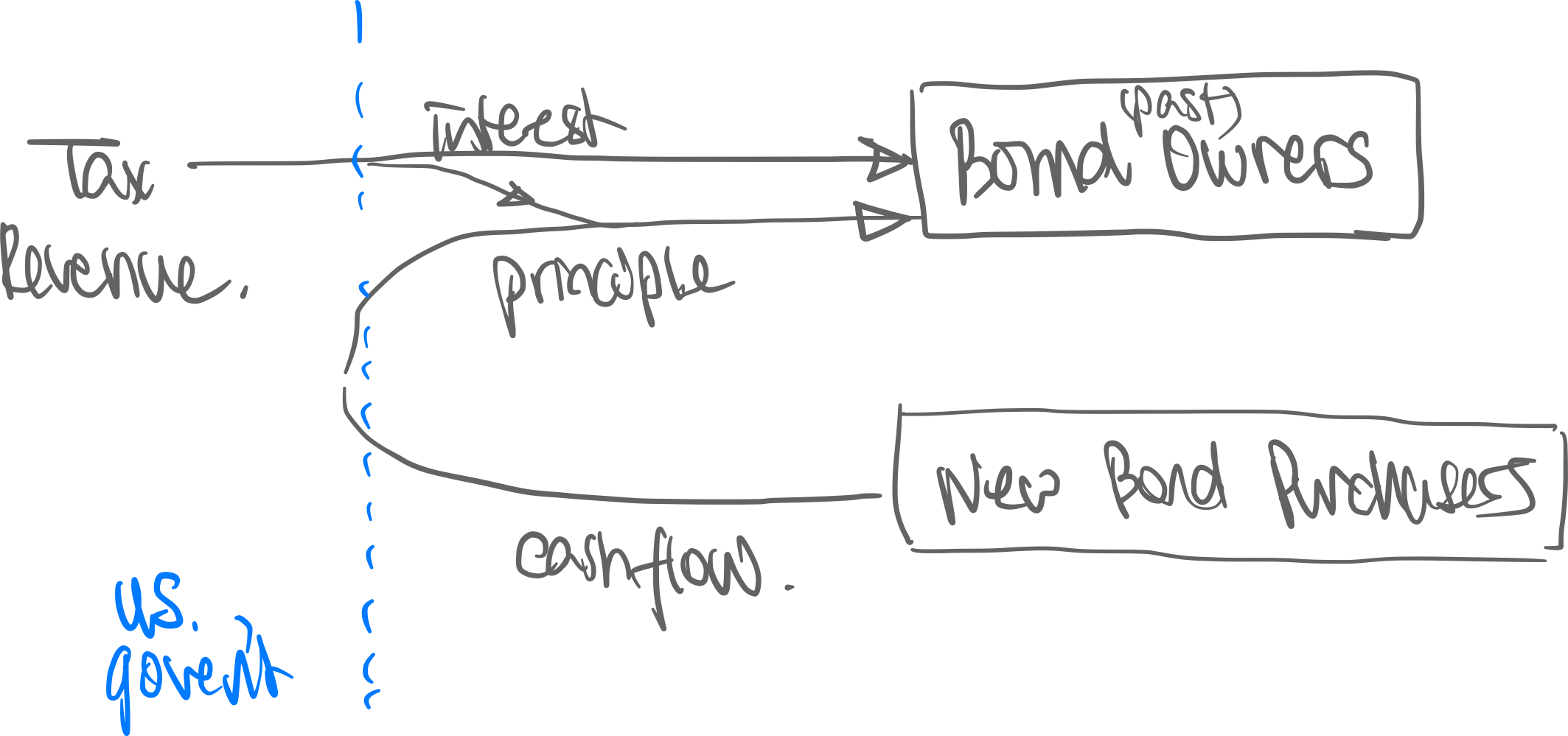
- Governments pay coupon and principal through
- Tax revenue
- Issuing more bonds
Bonds are an important part of a portfolio because…
- Are near-riskless investments as they generate stable cash flows. The only risks are: inflation risk—when the government doesn’t have the money, they’ll just print more money. This causes inflation which devalues the bonds.
- Are very liquid, since many people are willing to buy bonds in most scenarios, even in recessions.
Bond Pricing
thm. The price of a bond is the following:
where…
- is the current market price of the bond
- is the periods left to maturity (where is the years left to maturity)
- not periods passed! periods left
- is the Principal amount
- Normally use 1000
- is the per-period (=semi-annual) coupon payment
- normally, coupon is quoted at annual coupon rate (in percent) so
- (or ) is the yield to maturity (discount rate)
- is the current yield.
- is the number of coupon payments (semi-annual for Treasury bonds)
The Three Rates of Bonds
- : Yield to Maturity—“What’s the return rate for the coupons if I hold until maturity?”
- : Current Yield—“Coupon rate, but at the current bond price”
- : Coupon Rate—“Coupon rate (at principal price).”
- Price and rates:
- Trades at premium ⇔
- Trades at discount ⇔
Observe…
-
.
-
-
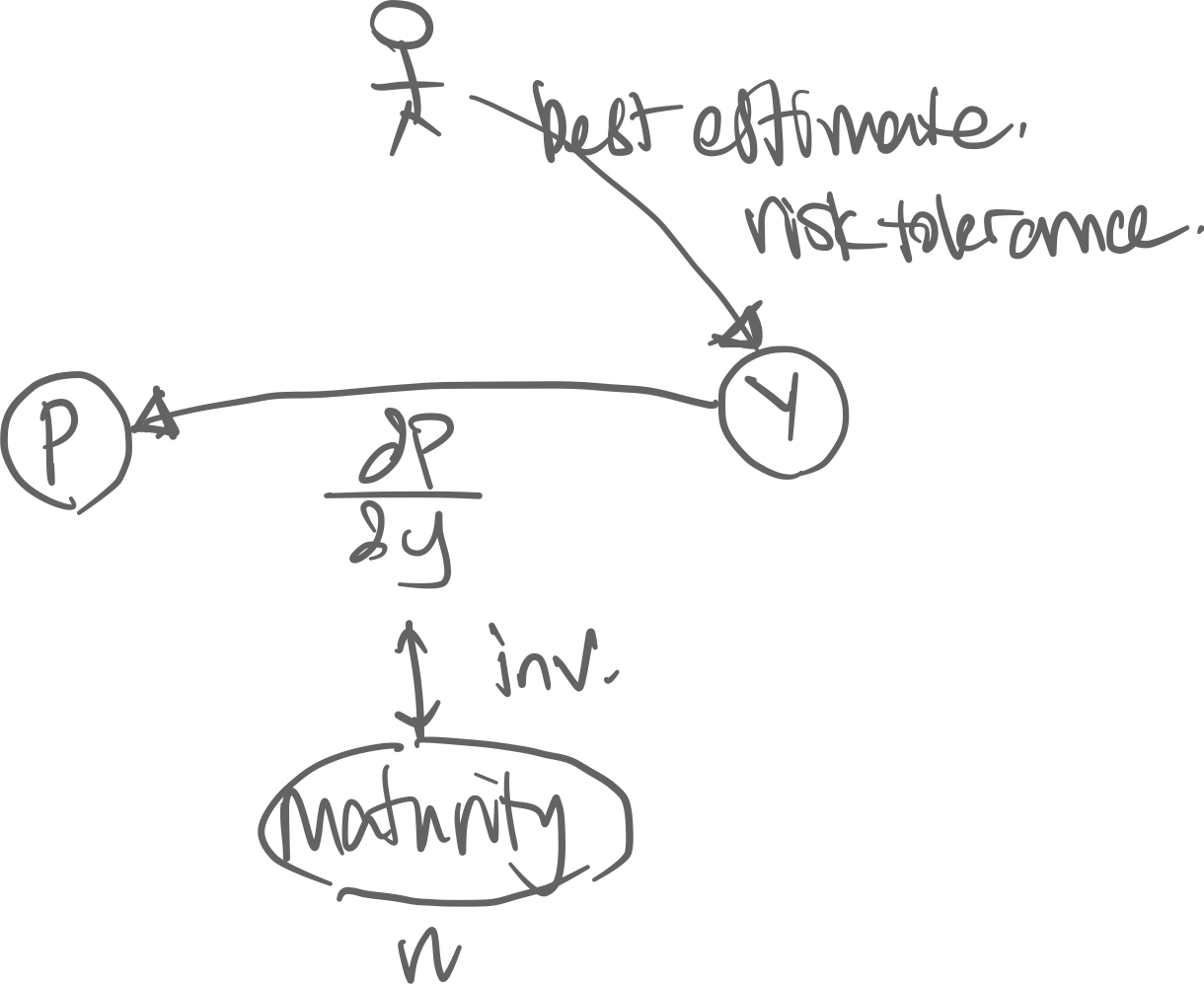
Causality: Exogenous factors → yield → price.
-
In a portfolio of bonds…
The causality of the variables of a bond. The market’s expected rate of return of a bond is the yield. With this yield we can calculate its price.
Price—Yield Curve (mathematical)
Price and Yield are inversly correlated → Price-yield curve looks like this:
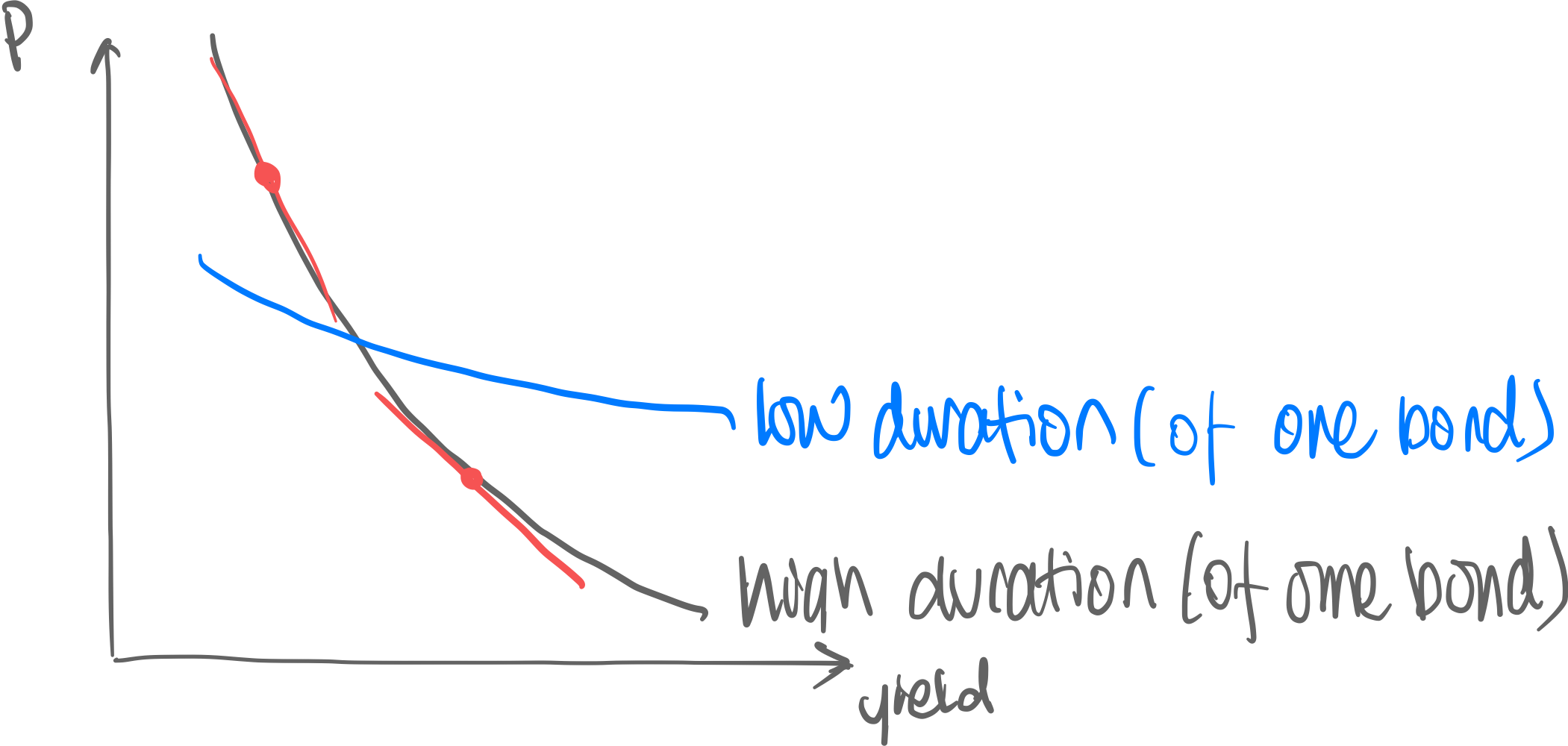
Duration is the gradient of this price-yield function:
Dollar Duration (DV01) is the change in price due to 1% change in yield [=$1 change in yield per par]
- Dollar Duration can be only used to approximate price changes for small changes in yield (~50bp)
- Duration is used to estimate risk (Price sensitivity against yield = DV01 risk
- Dollar Duration is quoted as an absolute value. (We all know that it’s mathematically negative)
- DV01 Risk:= = “ market value for 1% yield change” =
- DV01 has no relationship with volatility
Example calculation
| Time to Maturity | DV01 | Yield Vol. | e.g. change in yield | change in price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 year | $1.8 | 10%p | 20bp | $0.36 |
| 10 year | $7.2 | 5%p | 10bp | $0.72 |
Yield(–Maturity) Curve (empirical)
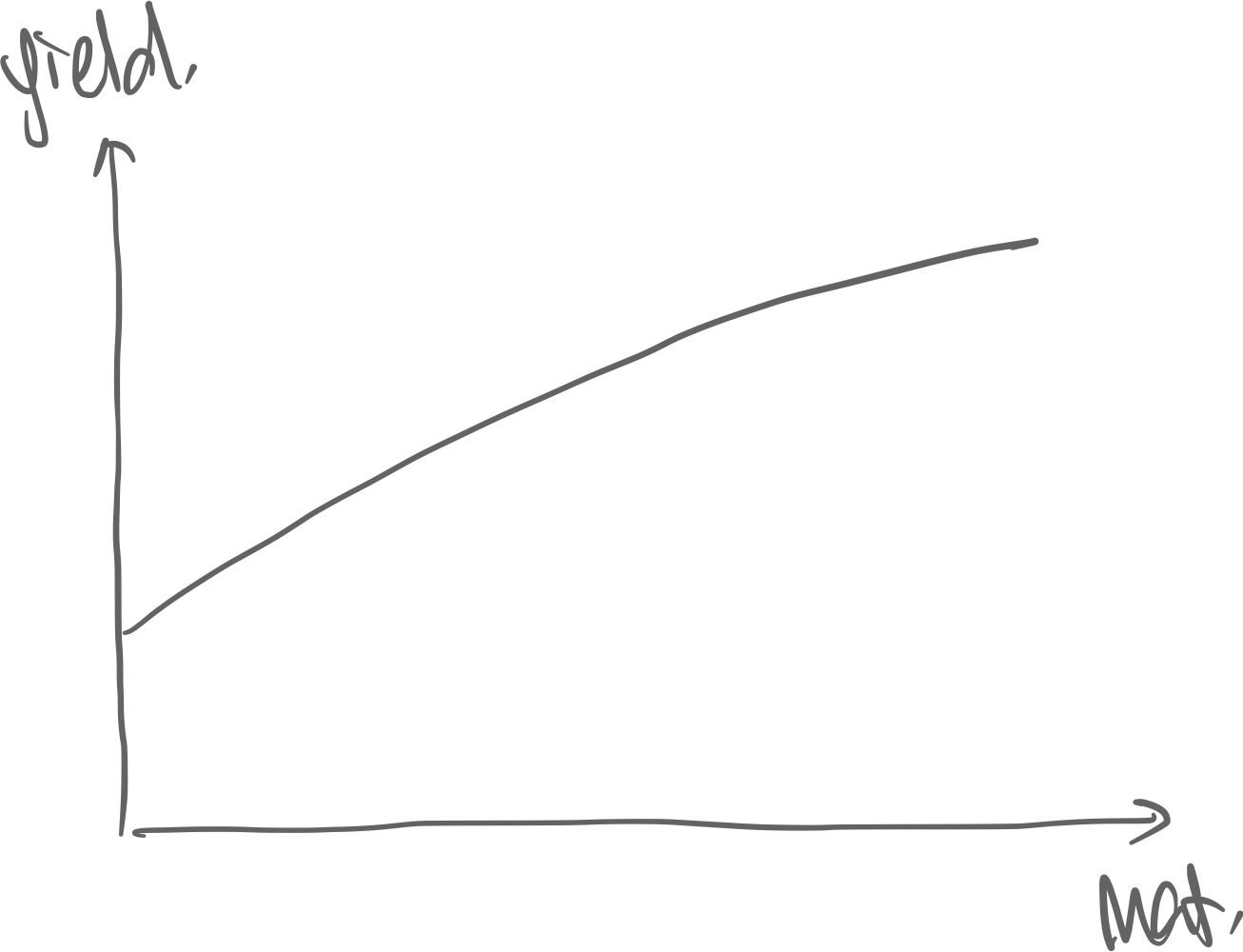

Determinors of the shape of the yield curve:
- Yield Maturity. The farther away the cash flows are, the more risky it is.
- Interest Rate changes. Yield 1/Price, and yield is linked to Fed Funds Rate. Thus buy at high yield, sell at low yield. Consider
- Bond investors think a recession is looming in 1yr → Treasury will increase rates in 1yr → sell 1yr mat bonds
- Left intercept is the fed rates & short-mat bonds → high movement right side is long-mat bonds → low movemen
- Liquidity Preference Theory. Shorter maturity bonds are more liquid simply because more of them exist in the world. Higher liquidity means less risk.
Risk & Volatility
def. Price[rate of return] volatility = (in $)
def. Yield volatility = (in %p)
def. DV01 Risk = Change in MV per change in 1% yield
- Yield Vol > RoR Vol ← mathematical relationship (price formula)
- Maturity Price Vol.