(DevonThink) 2. Relational Algebra
Mathematical formulation of operations on relational data.
- Made by E.F. Codd
- Equivalent to domain-independent relational calculus
- Relational calculus is a specialization of first-order logic
- Isn’t Turing-complete because it lacks recursion.
- But because of this, relational algebra is decidable
- High level and declarative (procedural implementation is left to DBMS)
- Easy to optimize by the DBMS
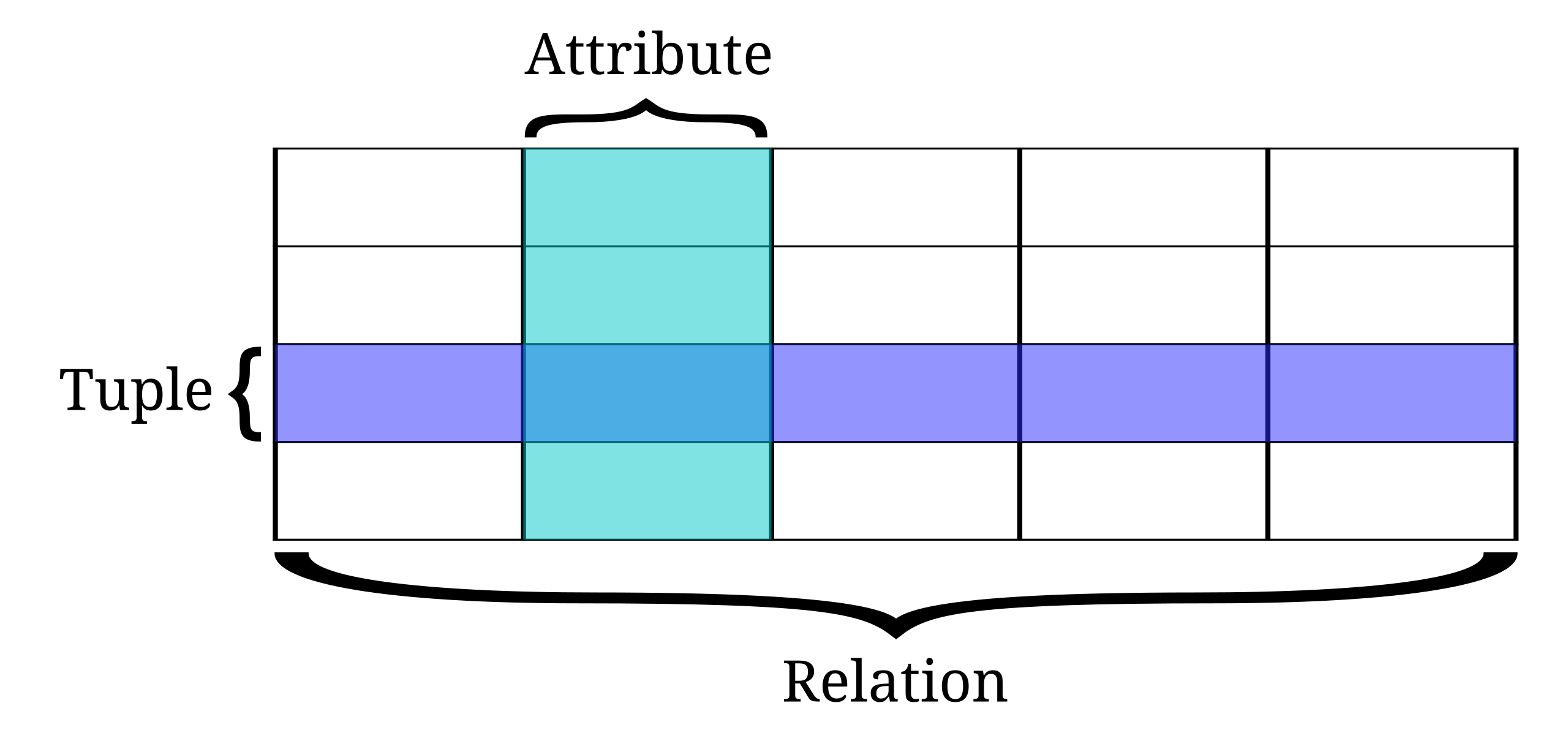
Definitions
| DBMS jargon | Common-sense name |
|---|---|
| Relation | Table |
| Attribute | Column |
| Domain | Data type |
| Tuple | Row |
- A row is defined as a tuple
- Duplicate rows are not allowed
- A tuple is considered same if all attributes are same.
- Schema: the tuple of attribute names (class)
- Instance: the instantiation of the schema (object)
- Key (see below for formal definition):
- e.g.
address(street_addr,city,state,zipcode)- ⇒
{street_addr,city,state}is a key- ..but
{street_addr,state}is not a key
- ..but
- ⇒
{street_addr,zipcodeis also a key
- ⇒
- e.g.
def. Superkey. A set of attributes is a superkey of relation if there exists a dependency:
def. Key. A superkey is a key of relation if there is no other superkey with smaller number of attribute elements. (=minimally identifies each tuple/row)
alg. Determining if a superkey is a key.
- Reduce one element and see if the key is superkey.
- If a reduction of one element doesn’t yield a smaller superkey, we got it.
- If it does, recurse.
Relational Operators
Fundamental Operations
- Selection:
- “Give me the entries of relation that satisfies condition ”
- Projection:
- “Give me the attribute for each entry of relation ”
- Duplicates are filtered out
- Cross Product:
- Same as cross product of normal sets.
- ⇒ Every row of per every row of
- Union:
- must have identical schema
- All rows on combined
- Duplicates are removed
- Difference:
- must have identical schema
- Rows in that are not in
- Renaming:
- Rename attribute of relation
Derived Operators
- Join [=Theta Join]:
- definition:
- “Cross Product the relations, and then filter by condition ”
- i.e. “Join the two databases so based on condition”
- Natural-Join:
- definition:
- where pairs common attributes
- where is the union of the attribute names
- “Theta join, but the duplicate attribute is removed”
- definition:
- Outer-Join
- Left outer join: (leave null entries from )
- Right outer join: (leave null entries from )
- Full outer join: (leave null entries from both)
- Intersection:
- must have identical schema
- defined as
- must have identical schema
- Symmetric Difference:
Monotonicity
(Vaguely related to: Monotonic Transformation)
def. Monotonic Operation. If input adds more rows, does the output also only add more rows? i.e. is a monotone operator iff:
- Difference () is the only non-monotone operator among simple operators
- Monotone for but not for
- If an operation is not monotone, it must include the difference operator.
Expression Tree Notation
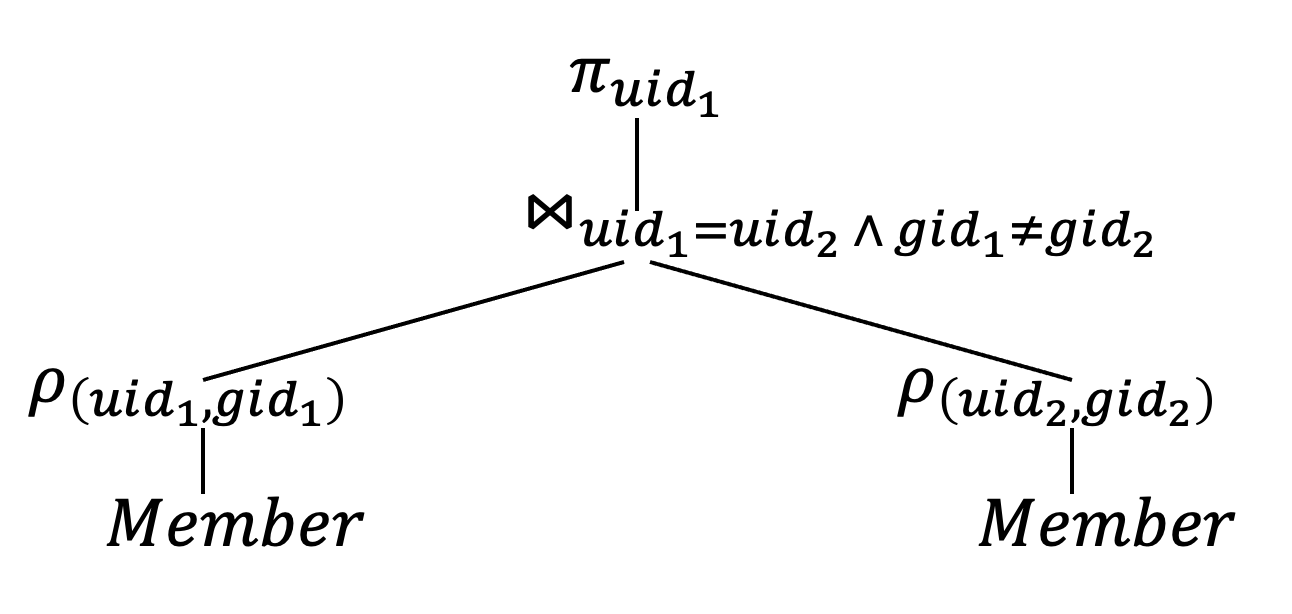
- Simpler to use and understand
- Designed both bottom-up or top-down
Properties of Relational Algebra
-
Selection Properties
- Idempotent:
- Commutative:
- Conjunction:
- Disjunction:
- Breaking up:
- Distribution over Difference:
- Distribution over Union:
- Distribution over Intersection:
-
Selection and Projection Commutativity
- where fields in
-
Projection Properties
- Idempotent: where
- Distributing on Union:
- ! Projection doesn’t distribute along difference:
- ! Projectio doesn’t distribute along intersection:
-
Rename Properties
- Distribution on Difference:
- Distribution on Union:
- Distribution on Intersection:
-
Product and Union
- Cartesian Product and Union: