Terminology
- : span; time taken for -processes with input size
- You may choose i.e. to analyze if unlimited parallelism was possible.
- : work; total time by all individual process;
- speedup: speedup factor compared to a single-process algorithm
spawn: start a new processsync: wait until all processes are finished
Parallel algorithms…
- For Memory Access Control we will concern ourselves with concurrent read & exclusive write model of computation
- are easy to make from recursive algorithms.
alg. PSum. Normal algorithm is . Following is a parallel algorithm:
function psum(l, r)
if l=r
return A[l]
spawn ls = psum(l, m)
spawn rs = psum(m+1, r)
sync
return ls + rs- Span:
- Parallel algorithm recursion tree:
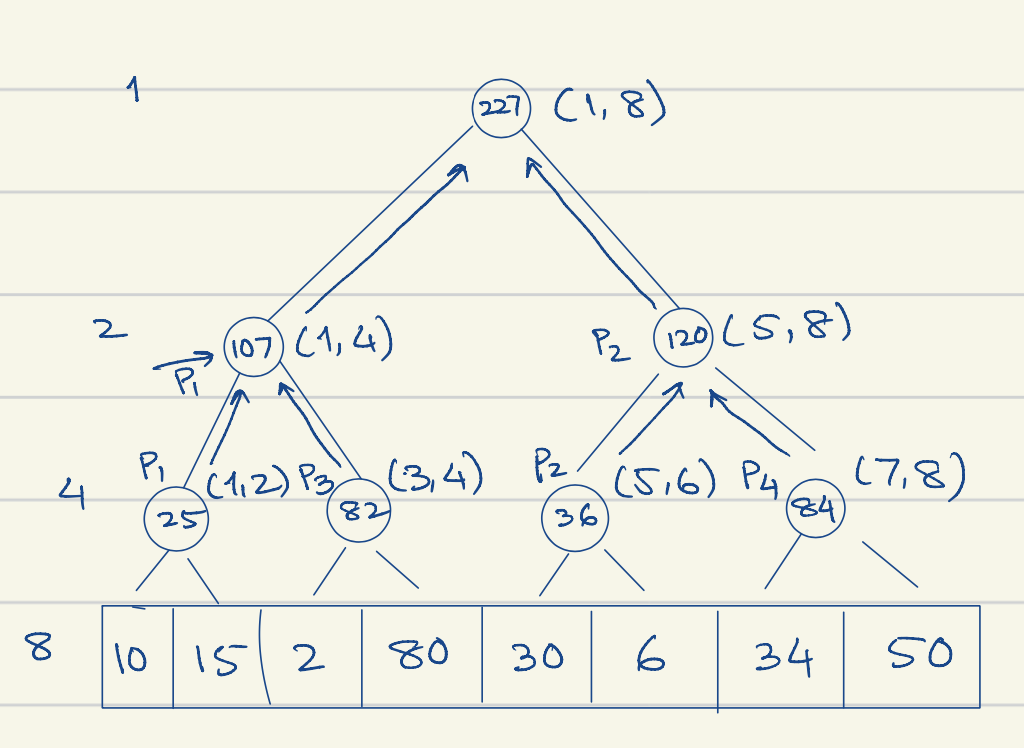
- depth is , each takes constant time ⇒
- …if number of processors are limited to , then:
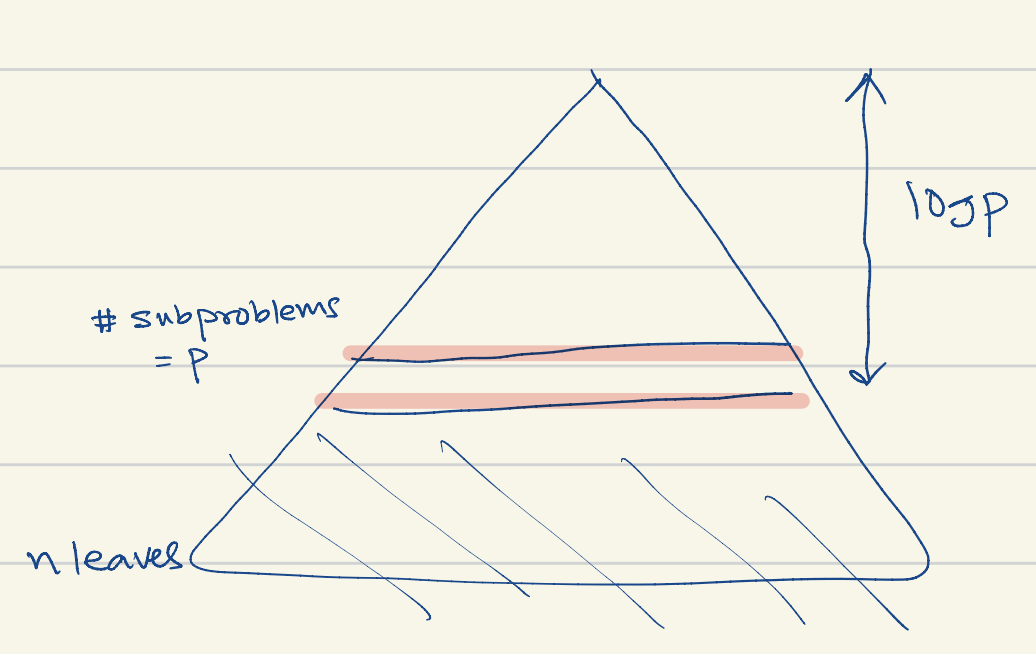
- where is the time for subproblems that cannot be parallelized (problem size is ) and is the parallel algorithm runtime.
- …if number of processros , then: