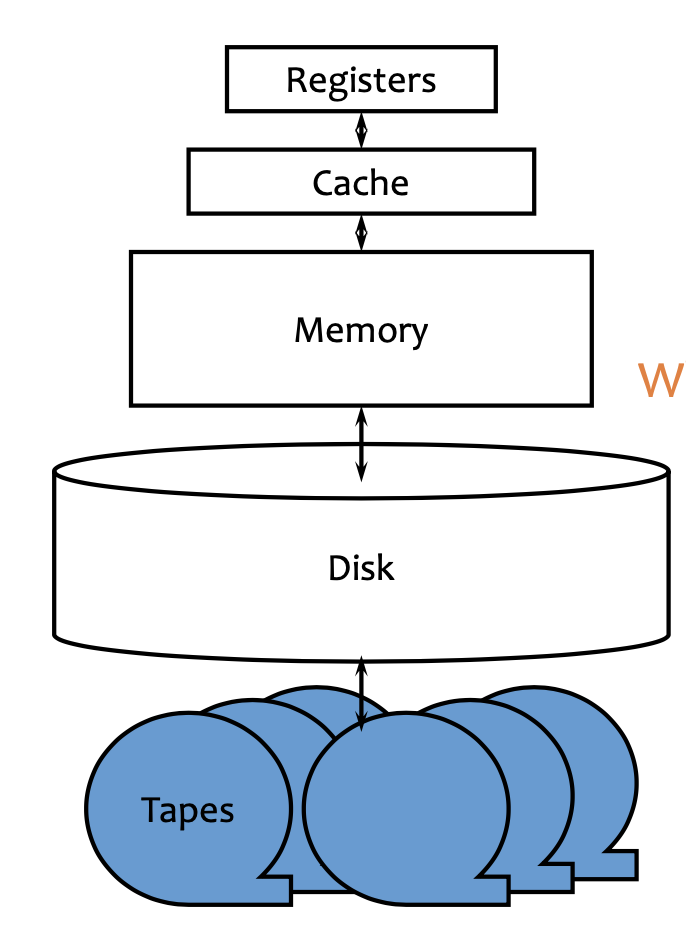
Anatomy of a Hard Drive §
- Parts of a mechanical hard drive:
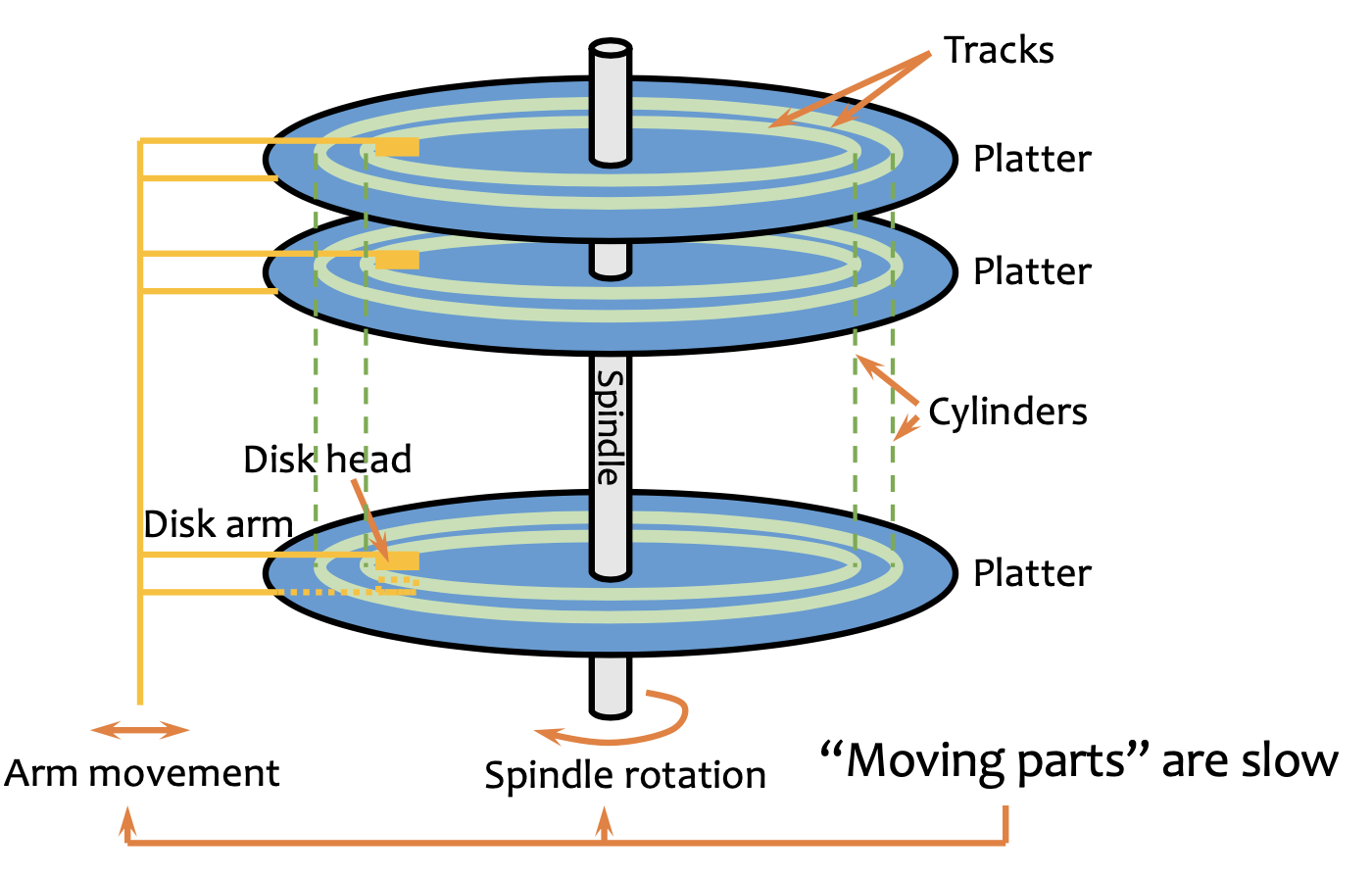
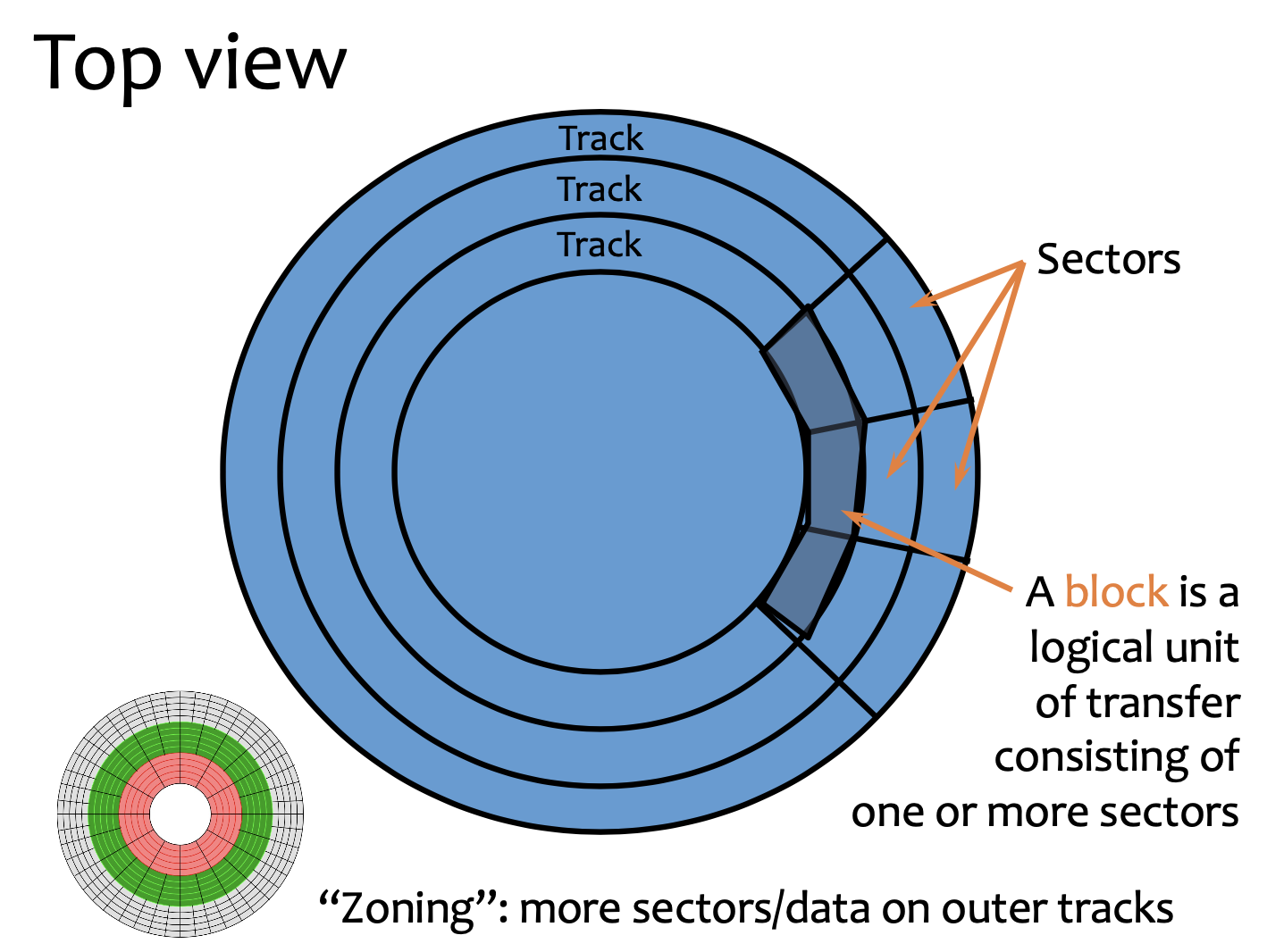
- Access Time=Seek+Rotation+Transfer
- All data is transferred in blocks! (512B~4KB)
- Records (=Tuples) can be fixed length of dynamic length
- BLOB fields: e.g. images. These link out to external locations
Storing Many Tuples in One Block §
- Often many tuples will fit in one block. There are multiple schemes to lay them out.
N-ary Storage Model (NSM) §
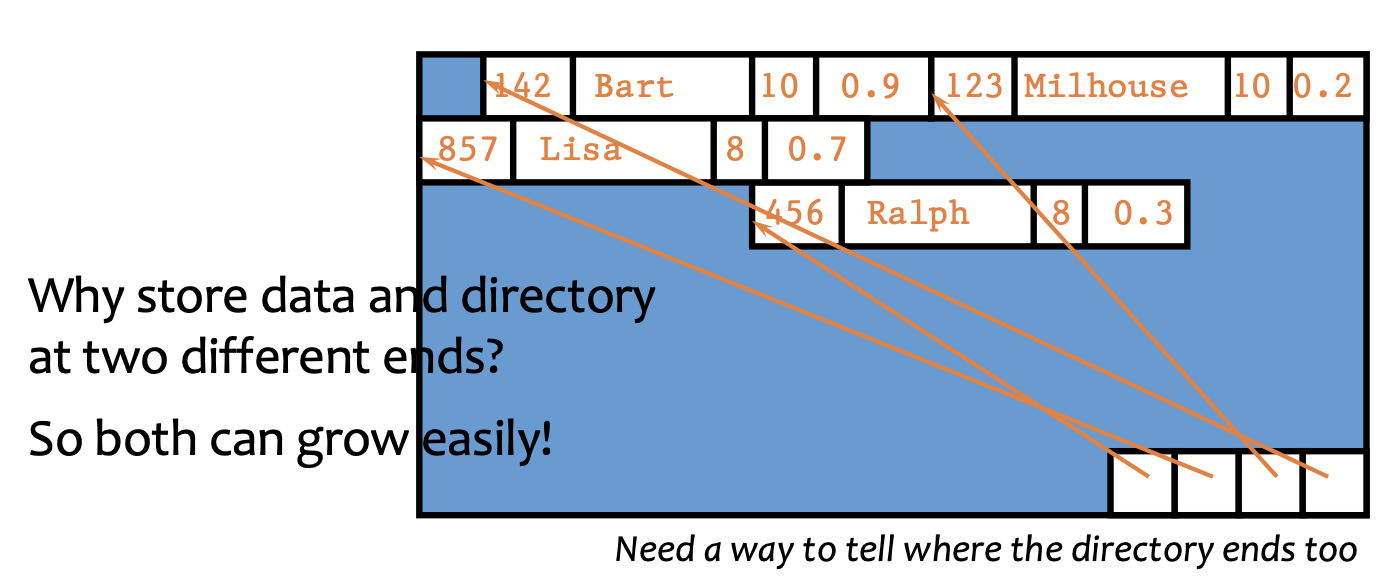
- Data stored from the beginning of the block
- Index stored at the end of the block
- Every update/delete operation will reorganize everything! → Use gaps inbetween records (=sparse block)
- Hard to cache, because queries will often only access a few columns
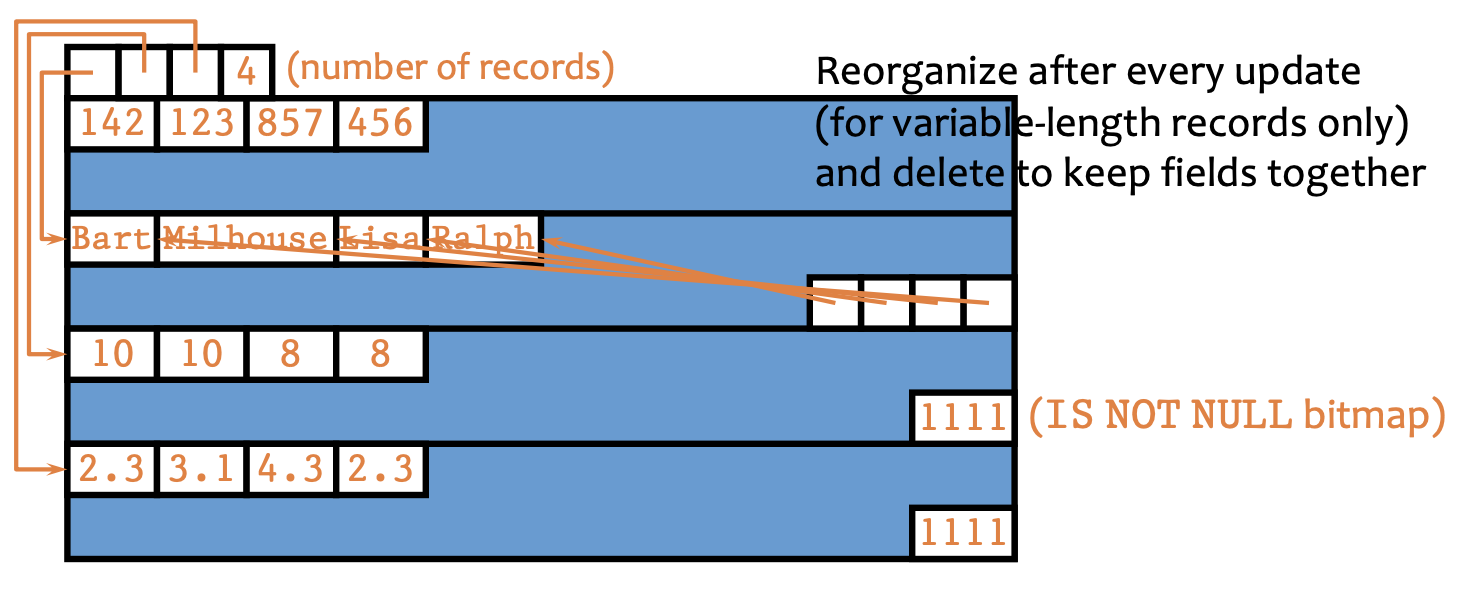
Partition Attributes Across (PAX) §
- Cluster columns together
- Variable length columns will have index at the end
- Keep the fields together (=dense block)
Column Stores §
- Store the whole table by columns
- e.g. Apache Parquet