Annuities are…
- Money you borrowed: mortgages, etc. ⇒ pay regularly to pay off large amount
- Money you lent: social security credit, etc. ⇒ give large money, get regular payments later
Amortization is the same thing but from a different perspective ⇒ You’re spreading a one-time cost into multiple years. Formulae are same if the recurring payments are of the same amount.
Types of Annuities
- Ordinary Annuity: payment occurs at the end of each period
- Simple Ordinary Annuity:
Formulae for Constant Payment
- : Term; time from first payment to last payment (in years)
- : Present value of annuity of terms.
- : Total payment accrued after periods (not a present value!)
- for formula simplification
- Preset value of annuity (=) formula. (see below for more)
- (i.e. the principal loan amount, mortgage loan amount, etc.)
- Payment accrued after all periods (= =Future value of annuity after all payments made) (Demonstration, use geometric sum formula)
- Simplified formula of PV using 1. and 2.
- Remaining balance after periods (=)
Portion of the -th payment that goes to… Principal
- Total Principal ⇒
Interest
- Every period, interest is fully paid.
- Interest is applied to the remaining balance (not to be confused with )
- Total Interest ⇒
⇒ Thus the total payment:
- Consider -periodic compounding (= times every year)
- Cost of Loan: ignoring the time value of money, sum of all interest payments
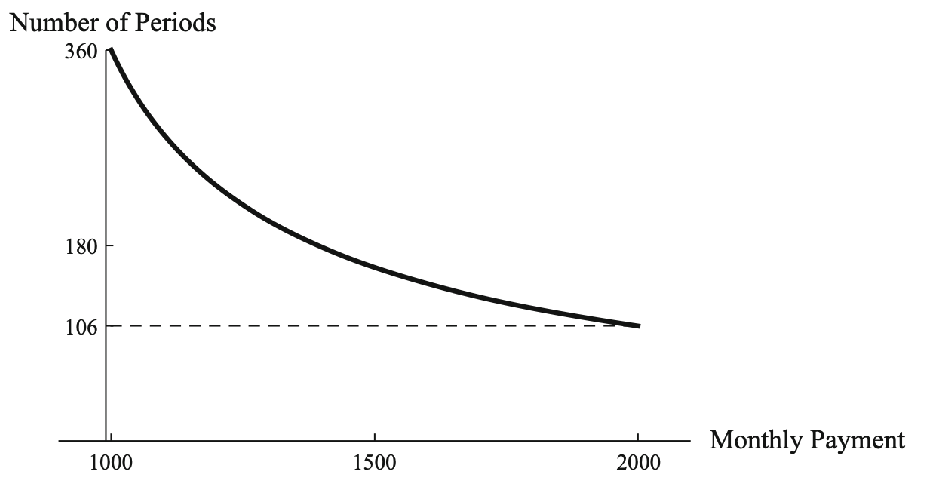
- As montly payment increases, number of payment periods decays exponentially.
Formulae for Variable Interest Rates
Variables are same as above, except:
- : payment after period
- : interest rate during period
- Present value of annuity ()