Long Run Input Demand
def. Ordinary Input Demand. Ordinary Demand for Inputs (=labor , capital )
- To derive: Profit Function
- Properties:
- HD0 in
- Decreasing in own-price ←regardless of anything! (Unlike Utility Maximization)
def. Conditional Input Demand. Demand of input (=labor , capital ) in order to produce a certain level out output
- HOWTO get: Cost Minimization
- Properties
- HD0 in input prices
- Decreasing in own-price
Short Run Input Demand
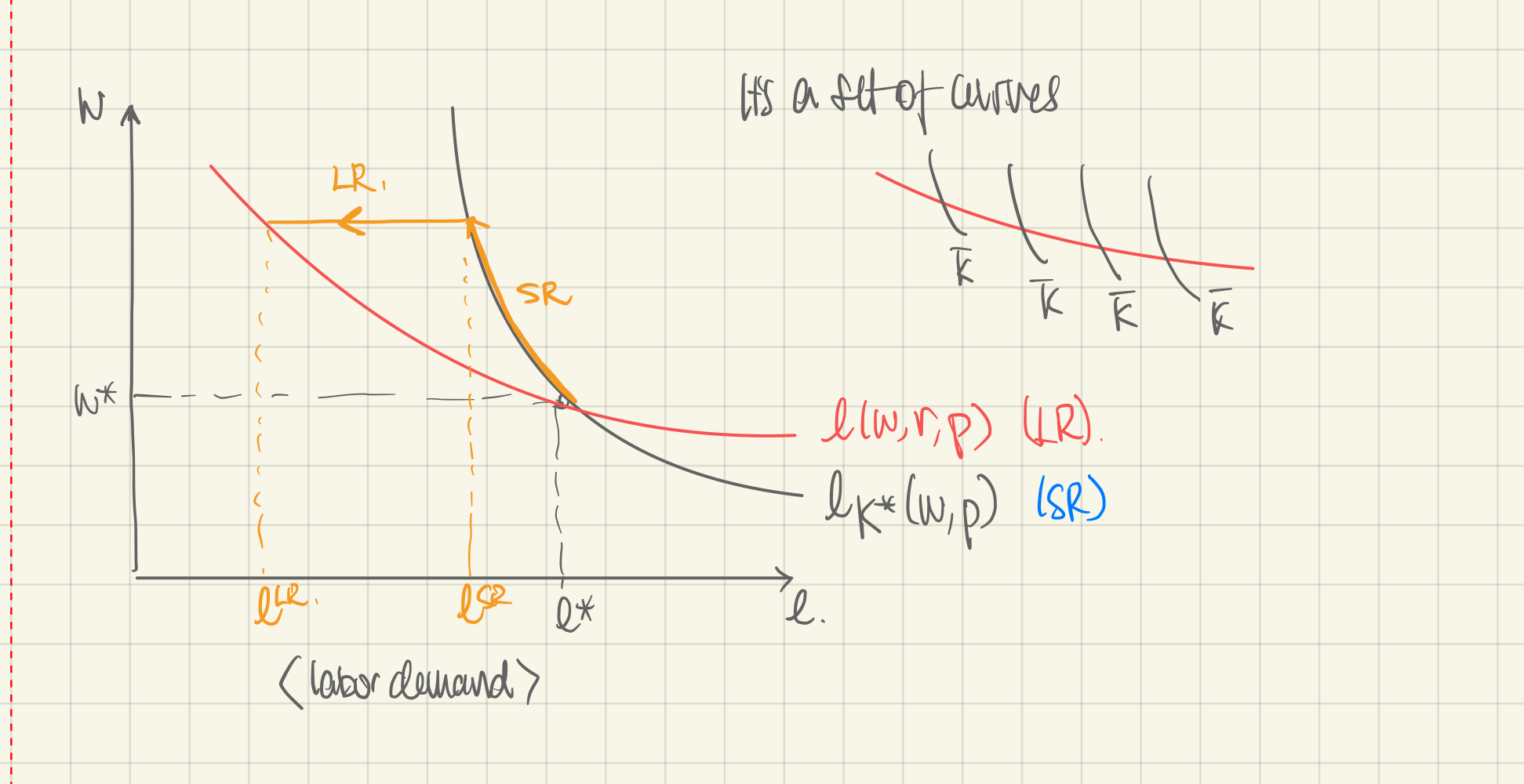
Short run (own-price) labor demand:
- is a parameter. Set it as the long-run input demand .
- In the short run, a change in or will only operate within with no change in possible.
- In the long run, we simply calculate the long-run input demand .
- Relationship between long-run input demand, visually:
Long Run Output Supply
def. Ordinary Supply. Relates the prices of inputs and output with the quantity of output produced
Properties
- HD0 in prices
- increasing in output price
- decreasing in input price
(HowTo) Derive Supply Function
Method 1:
- Get Input Demand and Output Supply from Profit Maximization
- Substitute into the Production Function
- Simplify to get . Method 2:
- Get cost function from Cost Minimization
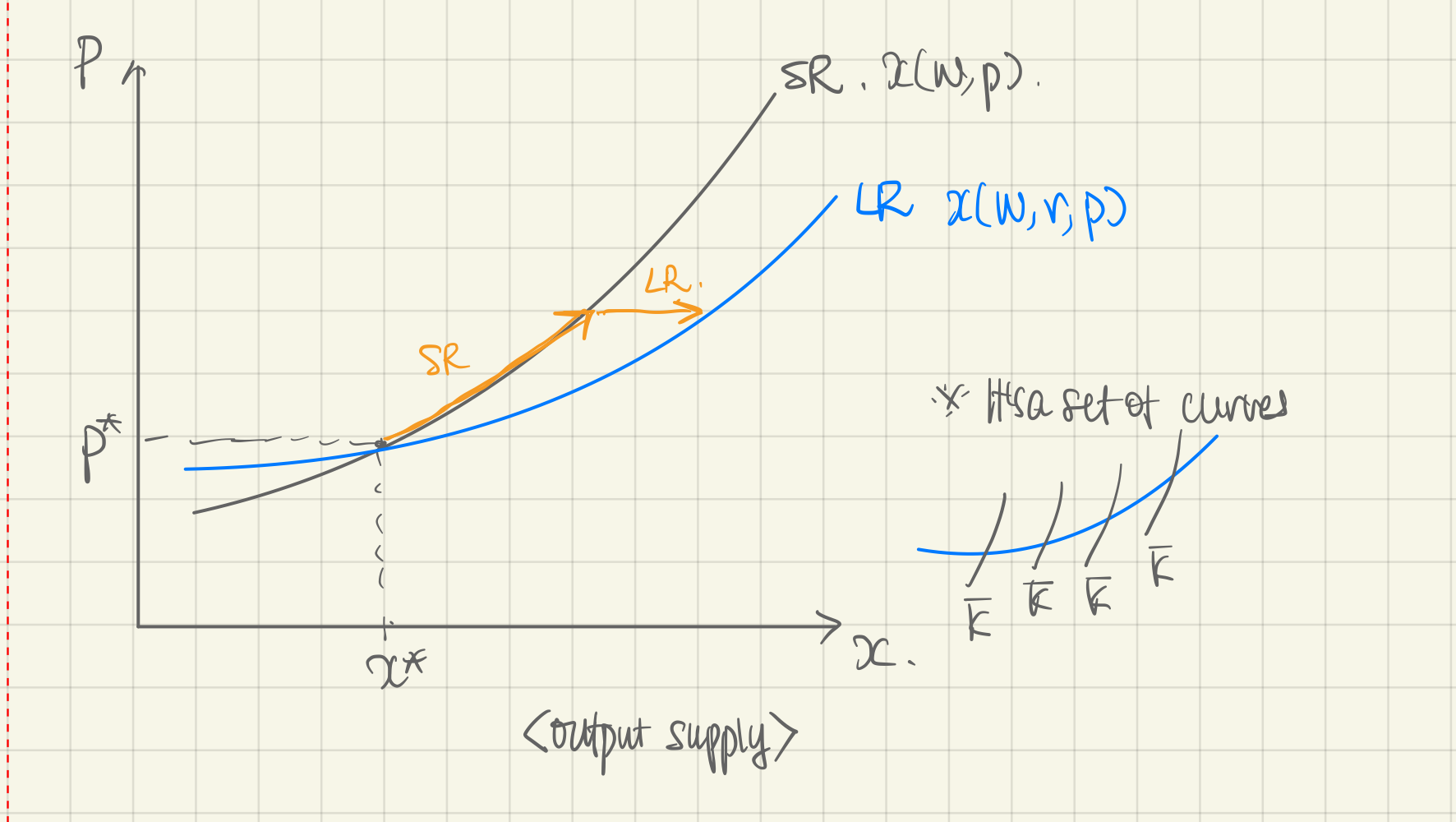
Short Run Output Supply
Short run (own-price) output supply:
- is a parameter. Set it to the long-run input demand
- Use the Production Function but with fixed.
- In the short run, a change in or will only operate within with no change in possible.
- In the long run, we simply calculate the long-run output demand .