thm. The price of a bond is the following:
where…
- is the current market price of the bond
- is the periods left to maturity (where is the years left to maturity)
- not periods passed! periods left
- is the Principal amount
- Normally use 1000
- is the per-period (=semi-annual) coupon payment
- normally, coupon is quoted at annual coupon rate (in percent) so
- (or ) is the yield to maturity (discount rate)
- is the current yield.
- is the number of coupon payments (semi-annual for Treasury bonds)
The Three Rates of Bonds
- : Yield to Maturity—“What’s the return rate for the coupons if I hold until maturity?”
- : Current Yield—“Coupon rate, but at the current bond price”
- : Coupon Rate—“Coupon rate (at principal price).”
- Price and rates:
- Trades at premium ⇔
- Trades at discount ⇔
Observe…
-
.
-
-
Causality: Exogenous factors → yield → price.
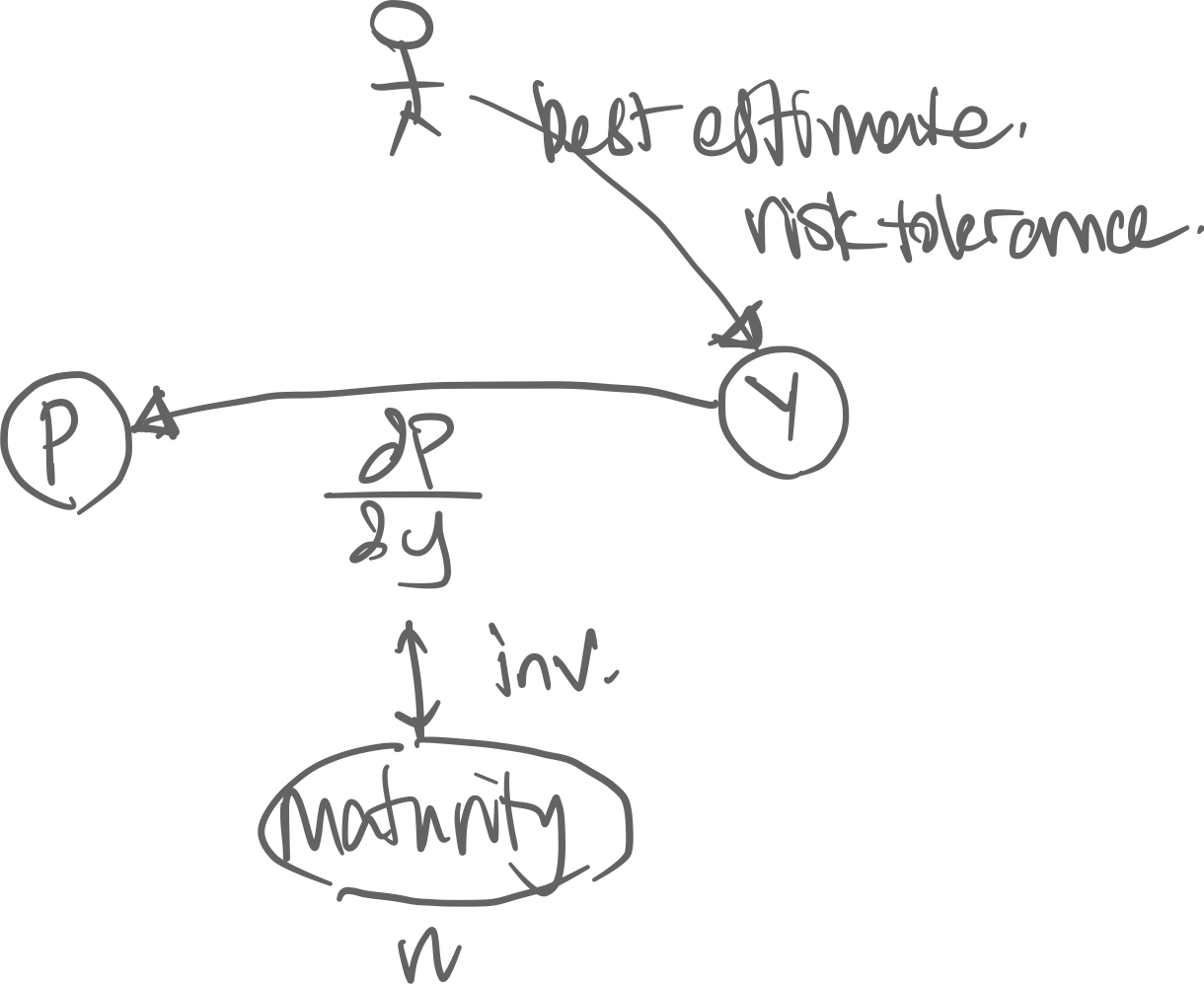
-
In a portfolio of bonds…
The causality of the variables of a bond. The market’s expected rate of return of a bond is the yield. With this yield we can calculate its price.
Price—Yield Curve (mathematical)
Price and Yield are inversly correlated → Price-yield curve looks like this:
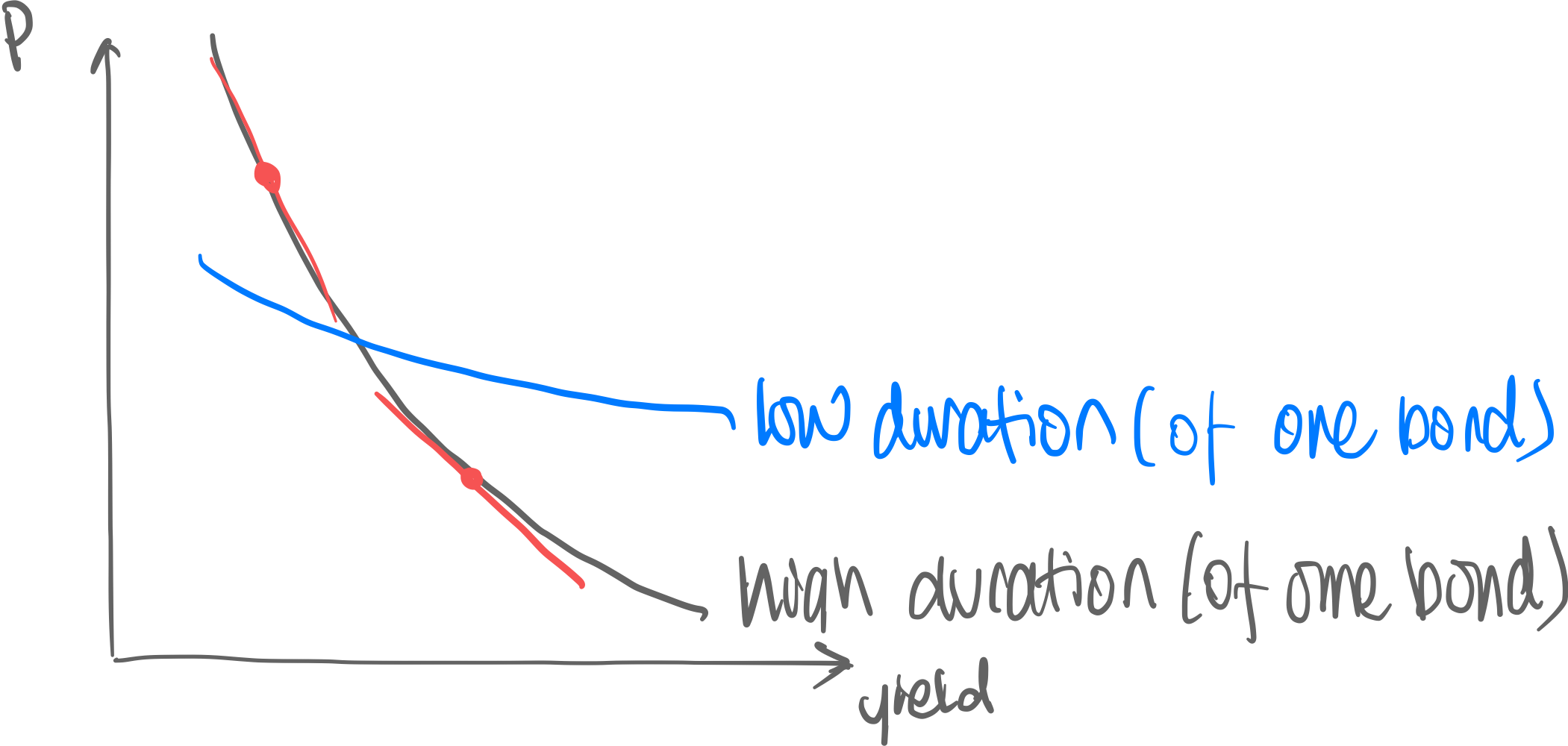
Duration is the gradient of this price-yield function:
Dollar Duration (DV01) is the change in price due to 1% change in yield [=$1 change in yield per par]
- Dollar Duration can be only used to approximate price changes for small changes in yield (~50bp)
- Duration is used to estimate risk (Price sensitivity against yield = DV01 risk
- Dollar Duration is quoted as an absolute value. (We all know that it’s mathematically negative)
- DV01 Risk:= = “ market value for 1% yield change” =
- DV01 has no relationship with volatility
Example calculation
| Time to Maturity | DV01 | Yield Vol. | e.g. change in yield | change in price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 year | $1.8 | 10%p | 20bp | $0.36 |
| 10 year | $7.2 | 5%p | 10bp | $0.72 |
Yield(–Maturity) Curve (empirical)
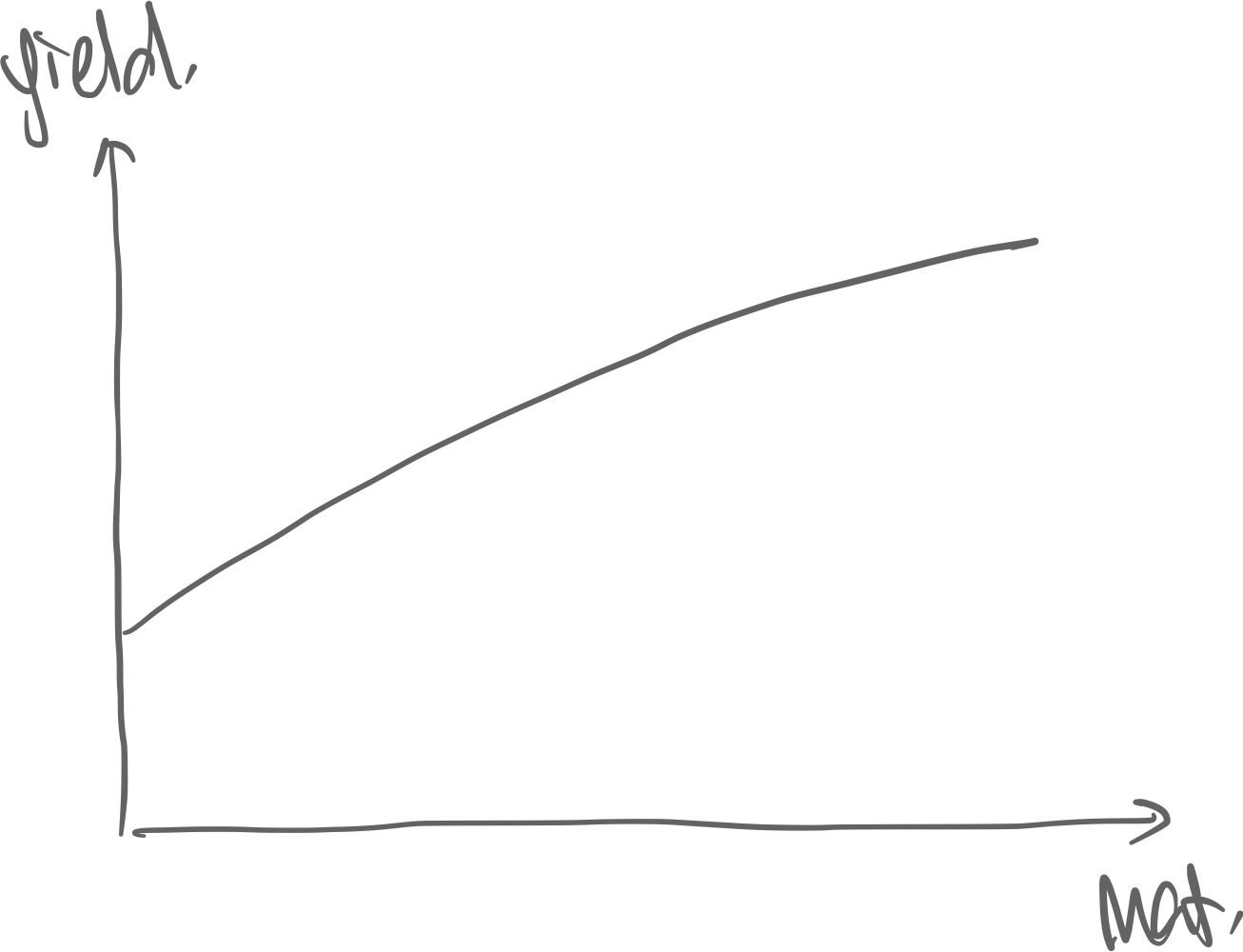

⇒ Yield Maturity, because the farther away the cash flows are, the more risky it is [ uncertainty]
- Inverted Yield Curve: Bond investors think a recession is looming → Treasury will increase rates
- Left intercept is the fed rates & short-mat bonds → high movement right side is long-mat bonds → low movement
Risk & Volatility
def. Price[rate of return] volatility = (in $)
def. Yield volatility = (in %p)
def. DV01 Risk = Change in MV per change in 1% yield
- Yield Vol > RoR Vol ← mathematical relationship (price formula)
- Maturity Price Vol.